Credit, or decrease, your cash account by the amount by which you must replenish the petty cash account in the journal entry. Subtract the amount by which you need to replenish the account from the total amount of your vouchers. A negative result represents a cash short amount, while a positive number represents a cash over amount.
Error
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- A firm should note instances of cash variances in a single, easily accessible account.
- Every time a register is short, the company’s expenses increase and profits decrease.
- In these cases, cash variances should be stored in a single, easily-accessible account.
- If the cash in the register is more than the sales there is said to be a cash over.
Here is a video of the petty cash process and then we will review the steps in detail. In the realm of financial management, pinpointing and reconciling cash over and short is a nuanced process that begins with the meticulous tracking of daily transactions. This involves comparing the expected cash amounts, based on sales data or receipts, with the actual cash present at the end of a business day. Discrepancies between these figures are indicative of an overage or shortage.

Is Cash Over and Short a Debit or Credit?
- When a cash discrepancy arises, a thorough investigation is imperative to unearth the root cause and prevent recurrence.
- Now subtract the amount remaining from the account’s original balance to determine by how much you need to replenish the account.
- Assume the same situation except that I receive $94 instead of $96 for the sale.
- Cash shortages are recorded in a separate income statement expense account usually known as the cash short or over account.
- If a cashier or bank teller errs by giving too much or too little change, for example, then the business will have a “cash short” or “cash over” position at the end of the day.
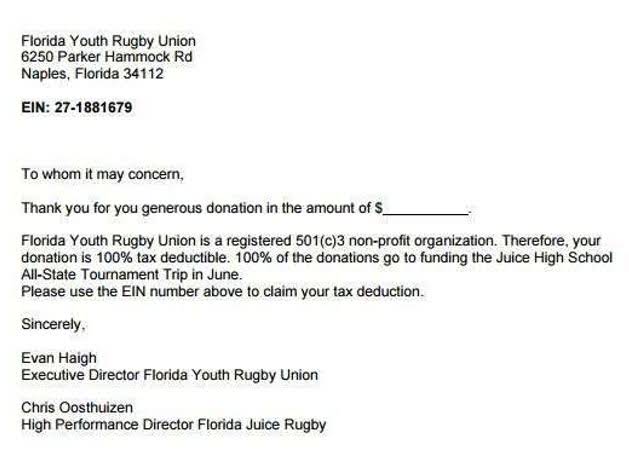
These errors cause the cash in the fund to be more or less than the amount of the fund less the total vouchers. When the fund is replenished, the credit to Cash is for the difference between the established amount and the actual cash in the fund. Any discrepancy should be debited or credited to an account called Cash Over and Short. The Cash Over and Short account can be either an expense (short) or a revenue (over), depending on whether it has a debit or credit balance.

Financial Accounting
The cash overage/shortage account is an expense account in the income statement of the business. Cash overages are normally recorded in a separate income statement expense account often referred to as cash short and over the cash over/short account. Once a discrepancy is detected, the next step is to reconcile the difference. This task typically falls to accounting personnel who must scrutinize transaction records, including sales receipts, refund documentation, and deposit records.
- These discrepancies are not just numerical errors; they have real implications for businesses.
- (Sometimes we refer to this fund as an imprest fund since it is replenished when it becomes low.).
- By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and accountability, businesses can minimize the likelihood of cash handling errors.
- In contrast, if we give too little change of cash to customers that means it is a gain for us.
- Usually one individual, called the petty cash custodian or cashier, is responsible for the control of the petty cash fund and documenting the disbursements made from the fund.
A key component of this framework is the segregation of duties, which ensures that no single individual has control over all aspects of a financial transaction. This division of responsibilities reduces the risk of errors going undetected and deters fraudulent activities. The cash over and short is recorded on debit when there is a shortage. In contrast, the cash over and short is recorded on credit when there is overage. In this article, we cover how to account for the cash short and over; especially on the cash over and short journal entry. Making sure that your books are balanced accurately is essential for managing the financial health of your business.
Note that the entry to record replenishing the fund does not credit the Petty Cash account. In this case, the cash needed to get back to $100 ($100 fund – $7.40 petty cash on hand) of $92.60 equals the total of the petty cash vouchers. In this case one balance sheet asset (cash), has been increased by 1,488 when the cash is banked.
Replenishing Petty Cash

Companies replenish the petty cash fund at the end of https://www.bookstime.com/ the accounting period, or sooner if it becomes low. The reason for replenishing the fund at the end of the accounting period is that no record of the fund expenditures is in the accounts until the check is written and a journal entry is made. (Sometimes we refer to this fund as an imprest fund since it is replenished when it becomes low.). To determine which accounts to debit, an employee summarizes the petty cash vouchers according to the reasons for expenditure. The journal entry to record replenishing the fund would debit the various accounts indicated by the summary and credit Cash. Sometimes, the petty cash custodian makes errors in making change from the fund or doesn’t receive correct amounts back from users.
Income Statement
When we give too much change to customers, https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ it means that we make change more than it should be. Thus, it is a loss as we give much more change of cash to customers. The cash short/over account is an expense account in the income statement of the business. A cash shortage normally occurs in a retail environment when the sales are reconciled to the cash receipts in the register at the end of the trading day.
What Does Cash Over Short Mean?

These procedures help to verify that the reported cash levels are accurate and that internal controls are being followed. Audits, whether conducted internally or by external parties, provide an objective review of financial practices and can identify areas for improvement. Surprise cash counts add an additional layer of security by preventing employees from preparing for the count, which can help to uncover any discrepancies that might otherwise be concealed. Cash over and short scenarios often stem from a variety of operational mishaps. Human error is a frequent contributor, with cashiers sometimes entering incorrect amounts into registers or giving improper change.